Slmgr ist ein Skript von Microsoft, mit dem ihr per Eingabeaufforderung den Windows-Key ändern, deaktivieren oder installieren könnt. Wir zeigen euch, was die einzelnen Befehle „rearm“, „ipk“, „ato“ und „upk“ bedeuten und wie ihr Slmgr nutzen könnt.
Video | 5 Tipps für Windows 10
Slmgr vbs – Syntax
Slmgr.vbs ist ein Skript in Windows das sich in erster Linie an Unternehmen mit Volumenaktivierung richtet. Ihr könnt es über die Eingabeaufforderung öffnen und Aktionen mit dem Windows-Key durchführen. Wie zeigen euch, wie das geht anhand der folgenden Parameter.
Die Syntax des Befehls sieht dabei so aus:
- slmgr (MachineName (Username Password)) (Option)
Ihr könnt mit dem Skript Slmgr also auch Remote-Computer verwalten, die sich im Netzwerk befinden.
Slmgr rearm
Standardmäßig lässt sich Windows 7 beziehungsweise Windows 8 ganze 30 Tage ohne Aktivierung nutzen. Ihr könnt den Zeitraum aber hinauszögern mit dem Befehl Slmgr rearm. So geht's:
- Öffnet eine Eingabeaufforderung mit Administratorrechten: Windows 10: Eingabeaufforderung öffnen und nutzen - So geht's.
- Tippt den Befehl ein und bestätigt mit der Eingabetaste: slmgr -rearm
!["Slmgr -rearm" setzt die Aktivierungsfrist in Windows zurück. "Slmgr -rearm" setzt die Aktivierungsfrist in Windows zurück.]()
- Startet Windows danach neu.
- Der Aktivierungs-Countdown wurde nun erneut auf 30 Tage gesetzt.
Hinweis: Ihr könnt den Befehl nach Ablauf der ursprünglichen Aktivierungsfrist maximal 3 mal ausführen. Dadurch ergibt sich eine Windows-Nutzung ohne Aktivierung von insgesamt 120 Tagen.
Slmgr ipk
Wenn ihr einen Windows-Key installieren wollt, könnt ihr das über den Befehl Slmgr ipk tun. Ipk steht dabei für Install Product Key. So geht's:
- Öffnet die Eingabeaufforderung mit Administratorrechten, wie oben beschrieben.
- Tippt danach den Befehl ein: slmgr -ipk xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx
Hinweis: Statt der X-Reihe gebt ihr den Product Key ein.
Slmgr upk
Ihr könnt über das Skript Slmgr.vbs auch Windows-Keys deinstallieren. Das ist etwa sinnvoll, wenn ihr den Key von einem PC auf einem anderen übertragen wollt. Dadurch ist Windows auf PC Nr. 1 nicht mehr aktiviert, dafür aber auf PC Nr. 2:
- Öffnet die Eingabeaufforderung mit Admin-Rechten und tippt den folgenden Befehl ein: slmgr -upk
- Upk bedeutet Uninstall Product Key.
Danach ist Windows nicht mehr aktiviert und ihr könnt den Key auf einem anderen Rechner verwenden. Eine genaue Anleitung findet ihr hier: Windows 10 deaktivieren – So geht's.
Slmgr ato
Mit dem Befehl Slmgr ato könnt ihr Windows online aktivieren. Dabei kommuniziert Windows dann mit dem entsprechenden Microsoft-Server. Sofern ein KMS-Server eingerichtet ist, wird Windows diesen stattdessen verwenden. Der Befehl ist hilfreich, wenn Windows sich wegen eines Verbindungsfehlers nicht aktiviert hat.
- slmgr -ato
Slmgr dti
Windows lässt sich auch offline ohne Internet-Verbindung aktivieren. Gebt dazu den Befehl in der Eingabeaufforderung mit Administratorrechten ein:
- slmgr -dti
- Euch wird dann eine ID angezeigt, mit der ihr Windows per Telefon aktivieren könnt.
![Der Befehl "slmgr dti" gibt eine Aktivierungs-ID aus. Der Befehl "slmgr dti" gibt eine Aktivierungs-ID aus.]()
- Ruft dann beim Microsoft Product Activation Center an und gebt die ID per Telefontasten durch.
- Ihr erhaltet dann eine Bestätigungs-ID.
- Tippt diese mit dem folgenden Befehl in die Eingabeaufforderung ein: slmgr -atp BESTÄTIGUNGS-ID
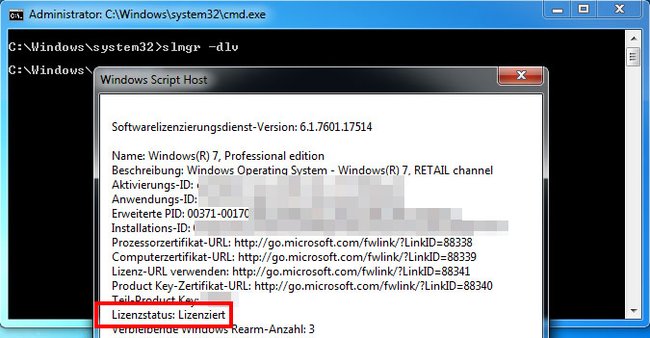
Slmgr dlv
Der Befehl prüft, ob eure Windows-Lizenz aktiviert ist. Ist das der Fall, zeigt das sich öffnende Fenster bei Lizenzstatus den Eintrag Lizenziert an.
Slmgr: Alle Befehle in der Übersicht
Alle Slmgr-Befehle zeigen wir hier nochmal in der Übersicht an:
slmgr | Erklärung |
-ato | Activate Windows license and product key against Microsoft's server. |
-atp Confirmation_ID | Activate Windows with user-provided Confirmation ID. |
-ckms | Clear the name of KMS server used to default and port to default. |
-cpky | Clear product key from the registry (prevents disclosure attacks). |
-dli | Display the current license information with activation status and partial product key. |
-dlv | Verbose, similar to -dli but with more information. |
-dti | Display Installation ID for offline activation. |
-ipk Key | Enter a new product key supplied as xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx. |
-ilc License_file | Install license. |
-rilc | Re-install system license files. |
-rearm | Reset the evaluation period/licensing status and activation state of the machine. |
-skms activationservername:port | Set the Volume Licensing KMS server and/or the port used for KMS activation (where supported by your Windows edition). |
-skhc | Enable KMS host caching (default), this blocks the use of DNS priority and weight after the initial discovery of a working KMS host. |
-ckhc | Disable KMS host caching. This setting instructs the client to use DNS auto-discovery each time it attempts KMS activation (recommended when using priority and weight). |
-sai interva | Sets the interval in minutes for unactivated clients to attempt KMS connection. The activation interval must be between 15 minutes and 30 days, although the default (2 hours) is recommended. The KMS client initially picks up this interval from the registry but switches to the KMS setting after the first KMS response has been received. |
-sri interval | Sets the renewal interval in minutes for activated clients to attempt KMS connection. The renewal interval must be between 15 minutes and 30 days. This option is set initially on both the KMS server and client sides. The default is 10080 minutes (7 days). |
-spri | Set the KMS priority to normal (default) |
-cpri | Set the KMS priority to low. |
-sprt port | Sets the port on which the KMS host listens for client activation requests. The default TCP port is 1688. |
-sdns | Enable DNS publishing by the KMS host (default). |
-cdns | Disable DNS publishing by the KMS host. |
-upk | Uninstall current installed product key and return license status back to trial state. |
-xpr | Show the expiry date of current license (if not permanently activated). |
Token-based activation: | |
-lil | List the installed token-based activation issuance licenses. |
-ril ILID ILvID | Remove an installed token-based activation issuance license. |
-stao | Set the Token-based Activation Only flag, disabling automatic KMS activation. |
-ctao | Clear the Token-based Activation Only flag (default), enabling automatic KMS activation. |
-ltc | List valid token-based activation certificates that can activate installed software |
-fta | Certificate Thumbprint . Force token-based activation using the identified certificate. The optional personal identification number (PIN) is provided to unlock the private key without a PIN prompt when using certificates that are protected by hardware (for example, smart cards). |



